Endurance training
- When you regularly exercise, body will adapt. 3-5 times a week, for few months.
- Adaptations depend on - frequency, intensity, duration, and type of exercise.
- Frequency
- Don’t be a weekend warrior when it comes to exercise.
- 3 to 5 days a week is ideal.
- Intensity is most important when it comes to adaptations.
- Use heart rate monitors.
- Intensity should be 50-85% of heart rate reserves.
- (heart rate reserve/100) * (max HR 210 - resting HR) + Rest HR
- Max HR = 220 - age
- For me to train at 85% HR reserve: 85%/100 * (220 - 37 - 66) + 66 = 165 bpm
- For me to train at 85% HR reserve: 50%/100 * (220 - 37 - 66) + 66 = 125 bpm
- Duration
- 20 to 60 mins of exercise.
- Type or mode
- Should involve large muscle groups.
- A training program should have
- Designated recovery days.
- Designated hard training weeks, followed by recovery weeks.
- Start with low intensity, lower duration and gradually increase both.
What happens when you stop training.
- Reversibility - all adaptations will be reversed with time once you stop training.
- Reversal of various adaptations is quite fast and will occur within weeks after training is stopped.
Strengh training
- Strength training adaptations depend on - frequency, intensity, number of repetitions per set, and number of sets.
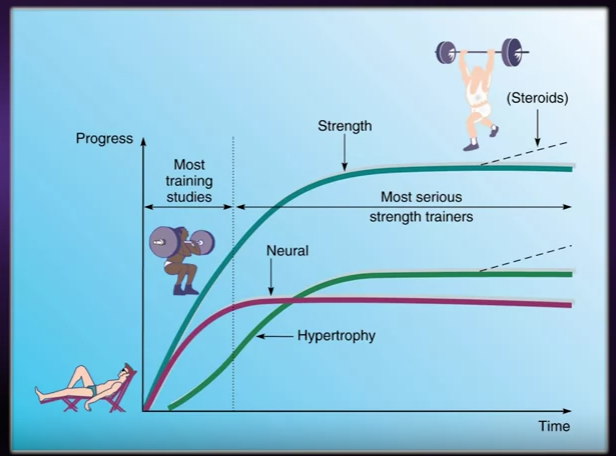
- After a period of strength training, output plateaus, factors affecting it
- Physical activity
- Nutrition
- Genetics
- Endocrine influences
- Nervous system
- Environmental.
- Growth hormones such as testosterone.

Differences for men and women in strength training.
- Men have more muscles and larger cross sectional areas.
- A man and a woman having same muscle mass can generate same amount of power and force.
- Due to very large quantities of testosterone (20-30 times), amount of muscle gain in men can be much higher.
Nutrition for training
- How much to eat?
- Endurance - weight stable.
- What to eat?
- Endurance
- Increasing carb stores.
- 55-60% calories from carbs.
- When?
- Takes 24 hours to replenish carb stores.
- First 1 to 2 hours post exercise.
- Pre-competition meal -
- 2 to 3 hours prior - reduces blood requirements of digestive system and stabilizes glucose level
- 300-500 calories, high in carbs.
Causes Of Muscle fatigue
- Muscle fatigue is inability to maintain output required during exercise.
- Common causes are located in the muscle itself.
- For Endurance exercise
- Depletion of carb stores.
- Calcium levels
- Body and muscle temperature.
Causes of muscle soreness
- During prolonged isometric contraction, blood flow to the muscle can be shut down, reducing oxygen flow.
- This results in creating ATP anaerobically, producing acids. These acids when released into blood stream cause localized burning and pain, which subsided quickly.
- Cramps - no clear reasons are yet established.
- Theory 1 - electrolyte imbalance.
- Theory 2 - bug in neural wiring.
- Can be solved using salts, fluids, massage and ice packs.
- Muscle soreness which starts hours after the exercise is caused by eccentric contraction, when muscle is stretched.
- These contractions causes micro tears in the muscle fibers leading to inflammation, weakness, tenderness, and pain.
- Damaged sarcomere (muscle tissues) are replaced with healthy.
- Subsequent exercise with same intensity with cause lesser pain.
- Blood doping - inject your blood cells before a competition.


