Week 9 Principles of Economics Microeconomics

Labour markets
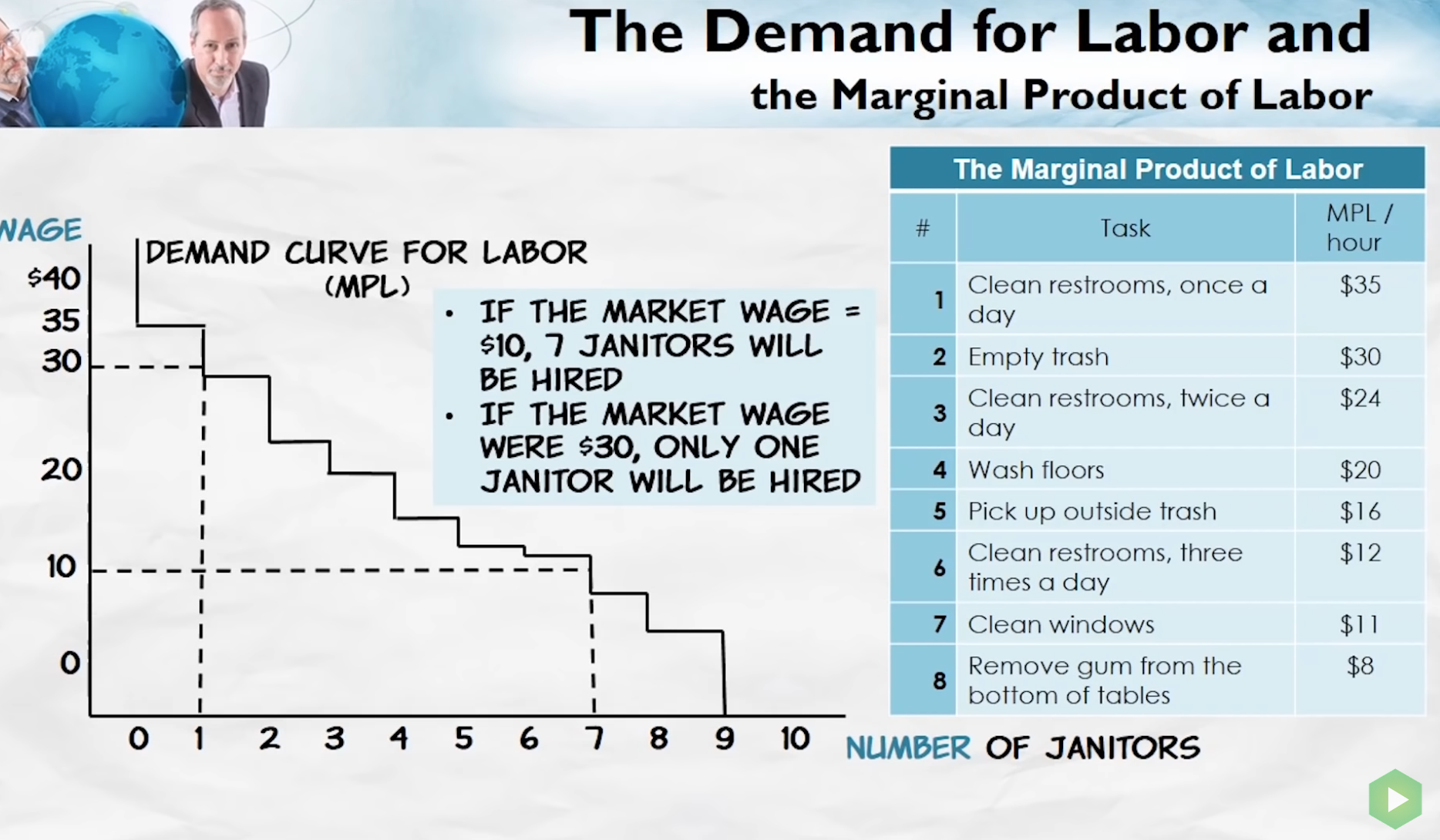
Marginal product of labour
- The increase in a firm’s revenue created by hiring an additional labourer.
- Declines with more labour.
- Firms hire as long as wage < marginal product.
Education
Is education just a signalling tool or does education provide real benefits?
- Earnings are co-related with having a college degree, even liberal arts degree.
- Not finishing a college does not add to future earnings, even if a person leaves college in the last year. This is the basic premise of signalling argument.
- Education does provide social contexts, building networks, learning skills which are not taught in a classroom.
Unions
- Western Europe despite having more unions than United States, has lower wages than the US.
- Unions raise wages by restricting supply of labour.
- Unions however are not just about wage negotiating, but general welfare of the workforce which does provide value.
Compensating differential
- If two jobs require the same set of skills, then wages at a more fun job will be less than wages at a less fun job.
- Wage captures not just the skill value of the labour, but also social characteristics of the job.
- Example - an optometrist in a remote Australian mining town makes far better wages than in a suburban Melbourne or Sydney.
- Wage also captures any other benefits derived from the job. If one job has more learning potential compared to another, wage at the job with higher learning will be less.
- Typically dangerous jobs have much higher wages than safe jobs.