Week 6 Principles of Economics Microeconomics

Trade
Benefits
- Trade makes people better off when preferences differ.
- Value to buyer > value to seller for a trade to happen.
- Specialization - boost productivity by creating skilled labour and information networks.
- It is not possible to know everything about everything. Specialization reduces amount of knowledge required to succeed.
- Developed countries have more combined knowledge than developing countries.
Globalization
Why is it good?
- Increases combined world knowledge.
Comparative Advantage - The more different we are from each other, the more we benefit from trade.

Opportunity cost
- Time and resources are finite.
- You want to maximize your payoff.
Summary
- In two country/person examples, trade makes everyone better off, but in larger examples some may be worse off.
- Comparative advantage applies to groups and individuals.
- Diversity is a strength when combined with trade.
Tariffs and Protectionism
Protectionism - economic policy of restraining trade through tariffs, quotas, or other regulations that burden foreign producer but not domestic.
Tariff - tax on import. Quota - Quantity restriction of import.
International trade
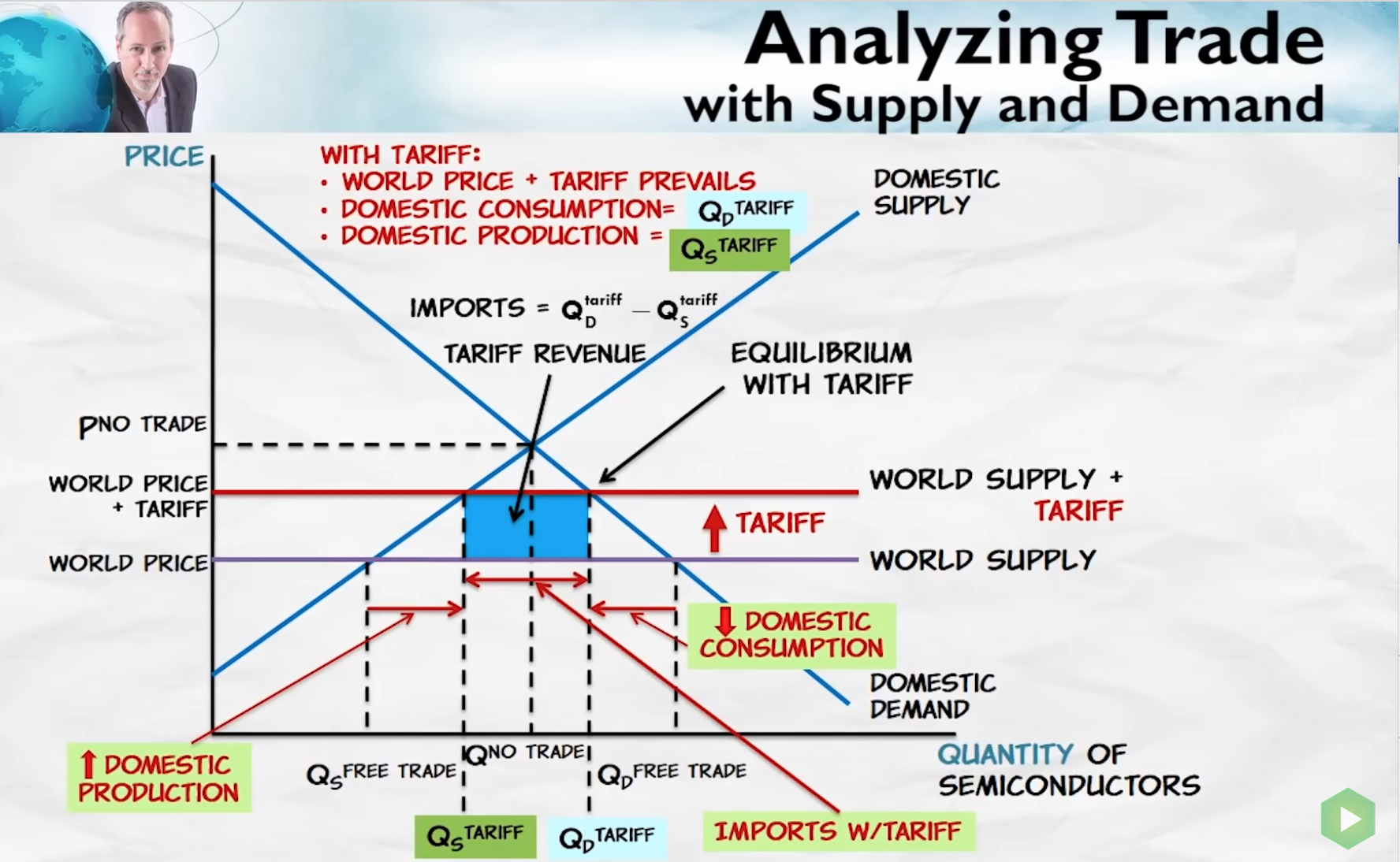
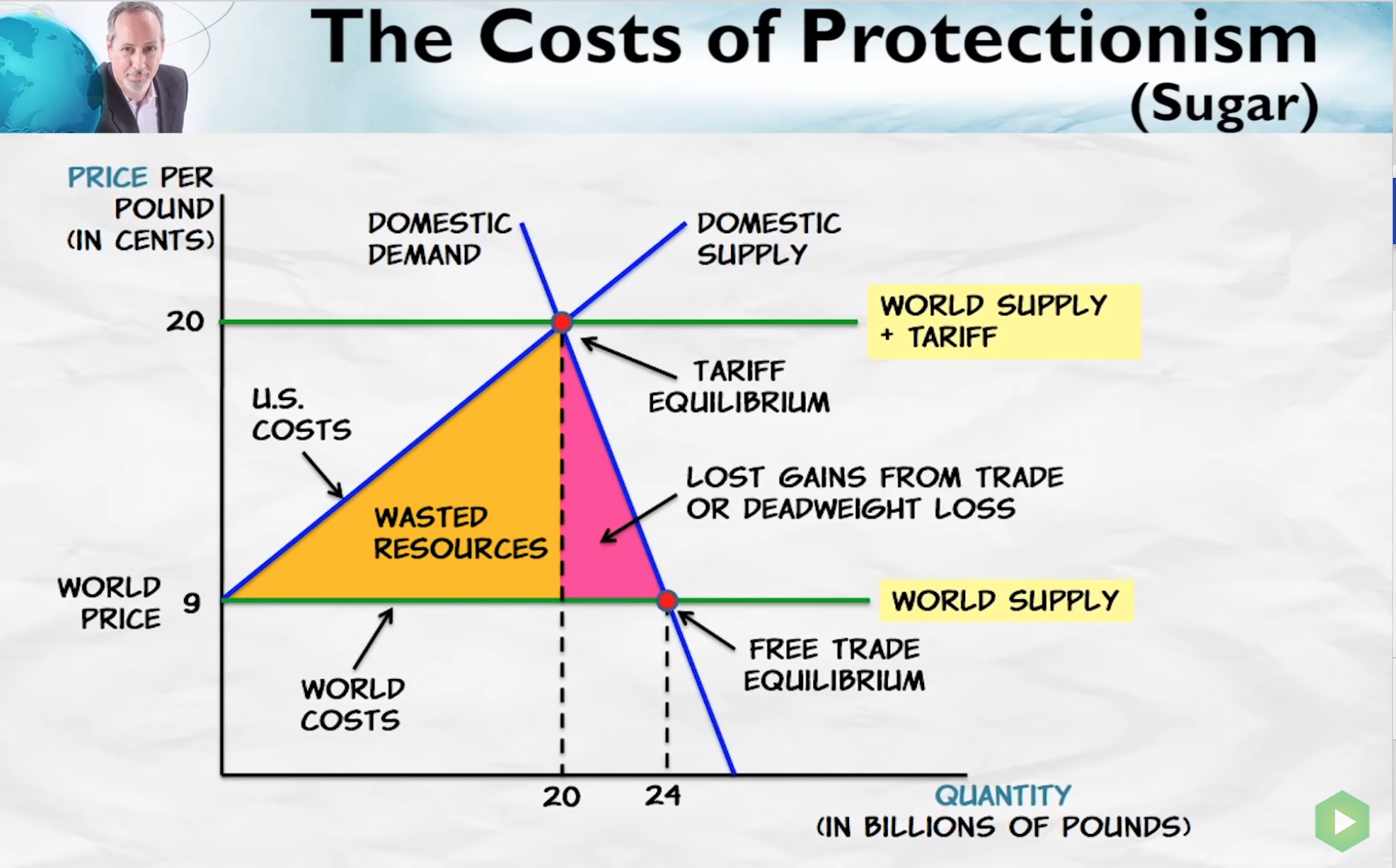
Effects of tariff that influence welfare
- Domestic consumption reduces.
- Domestic production increases.
Both of these reduce welfare because
- Domestic consumption reduces leading to lost gains from trade.
- Domestic production increases, leading to use of resources in products where they are not as valued under trade, leading to wasted resources.
Tariffs
- Increase price, create deadweight losses.
- Direct production from low-cost to high-cost.
Distribution of losses
- Bad for consumers.
- Good for domestic producers.
- Bad overall.
Arguments against international trade
Reduces domestic jobs
We pay for imports with exports!
- Trade moves jobs from import industries to exports.
- Wages increase on average due to comparative advantage.
- Problems do arise when low skilled jobs are lost and labour is not up skilled.
Child labour
- Child labour is a side effect of poverty.
- Restraining trade due to child labour will further increase poverty and put more children at risk.
- Trade however in the long run will increase wealth and reduce child labour.
National security
- Anything can be considered important for national security.
- Key industries at home - Maybe valid for very few industries. But supply chains for those are global and hence still difficult without trade.
Cost of protectionism